Uncover the truth what do termites really look like
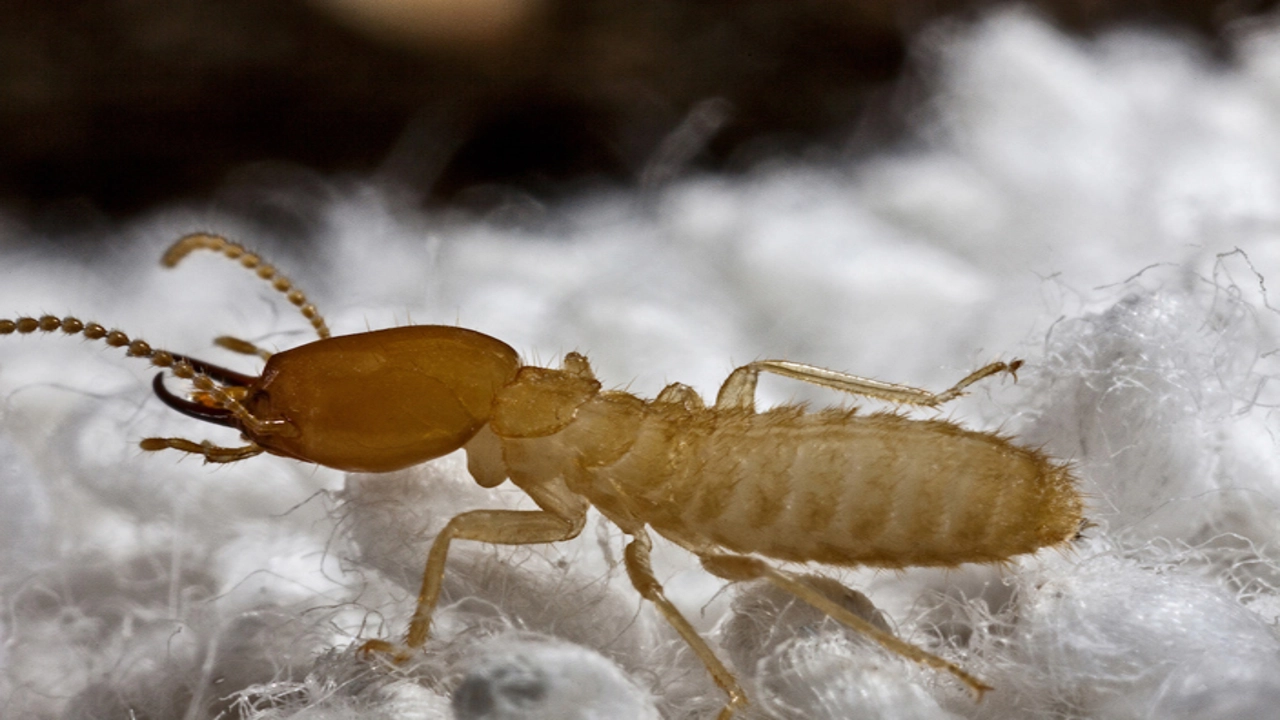
How do termites look like? These tiny insects, often mistaken for ants, are surprisingly diverse in appearance. While some species may be light brown or white, others can be darker, even black. Termites are typically small, ranging from 1/8 to 1/2 inch in length, with soft bodies and straight antennae. Workers are wingless and blind, while reproductive termites, known as alates, possess two pairs of long, straight wings. Identifying these pests is essential for early detection and prevention of damage to your home.
termites the hidden critters you won t believe exist
Termites are small, social insects that can cause significant damage to wooden structures. If you suspect you might have termites, it’s important to be able to identify them. How do termites look like? Understanding their appearance can help you determine if you have a termite infestation and take the necessary steps to address it.
Termite Types and their Distinguishing Features
There are different types of termites, each with slightly different characteristics. The most common types in the United States include:
- Subterranean termites: These are the most destructive type and are found throughout the country. How do termites look like in this case? Subterranean termites are pale, cream-colored, and soft-bodied. Workers are about 1/4 inch long, while soldiers have larger heads and powerful mandibles for defending the colony.
- Drywood termites: These termites are found in drier climates and prefer to infest dry wood. How do termites look like in this case? Drywood termites are slightly darker than subterranean termites, with a reddish-brown color. Workers are also about 1/4 inch long, while soldiers have a distinctive, elongated head.
- Formosan termites: This invasive species is found in the southeastern United States and is particularly destructive. How do termites look like in this case? Formosan termites are similar in appearance to subterranean termites, but they are slightly larger and have a more yellowish-brown color.
Common Characteristics of Termites
While each species has its own unique features, termites share several common characteristics that help distinguish them from other insects.
- Size: Termites are generally small, ranging from 1/8 to 1/2 inch in length.
- Color: Termites are typically pale, cream-colored, or brown, depending on the species.
- Shape: Termites have a soft, elongated body with a distinct head and abdomen.
- Antennae: Termites have straight, bead-like antennae.
- Wings: Termites have two pairs of wings that are equal in length. However, only reproductive termites have wings.
How to Tell Termites From Other Insects
There are several insects that can be easily mistaken for termites, especially for those unfamiliar with the differences. Here are a few key features that can help distinguish termites from other insects:
- Ants: While ants and termites are similar in size and color, termites have straight antennae, while ants have bent antennae. Termites also have a broader waist than ants.
- Carpenter ants: These ants can also be confused with termites, as they nest in wood. However, carpenter ants have a more defined waist, while termites have a broader waist.
- Other wood-boring insects: There are several other wood-boring insects, such as powderpost beetles, that can be mistaken for termites. However, these insects typically leave behind a fine powder, while termites leave behind frass, which is a mixture of wood and termite droppings.
Finding Termite Evidence
If you suspect you might have termites, it’s important to inspect your home for signs of an infestation. Look for:
- Mud tubes: Subterranean termites build mud tubes to travel between their nests and food sources. These tubes can be found on walls, foundations, or other areas where termites are active.
- Swarming: Termites swarm during the spring and summer to mate. Swarmers are reproductive termites with wings that are shed after mating. You may find shed wings near windows or doors.
- Frass: Termite droppings, known as frass, are small pellets that resemble sawdust.
- Wood damage: Termites can cause significant damage to wooden structures, including floors, beams, and furniture. Look for signs of damage, such as holes in wood, soft spots, or crumbling wood.
What to Do If You Find Termites
If you find evidence of termites, it’s important to call a qualified pest control professional as soon as possible. How do termites look like in your home? A professional can identify the type of termite you have and recommend the most effective treatment options. Termites are a serious threat to your home, and professional help is the best way to ensure they are eradicated.
Understanding Termite Behavior
Termites are social insects that live in colonies. Each colony has three main castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives. Workers are responsible for foraging for food, building the nest, and caring for the queen and young. Soldiers are responsible for defending the colony. Reproductives are responsible for mating and starting new colonies.
Understanding termite behavior can help you better understand how to identify and control them. For example, knowing that subterranean termites build mud tubes can help you locate their nests. Knowing that termites swarm in the spring and summer can help you prevent infestations by sealing up cracks and crevices.
Termite Control: Prevention and Treatment
Preventing termite infestations is important. This includes:
- Maintaining a dry environment: Termites thrive in moist environments, so it’s important to fix any leaks or water damage.
- Inspecting wood: Regularly inspect your home’s wooden structures for signs of termite damage.
- Removing woodpiles: Termites can use woodpiles as breeding grounds, so it’s important to remove them from your property.
- Using termite-resistant materials: When building or renovating your home, use termite-resistant materials, such as pressure-treated wood.
If you find termites in your home, it’s important to seek professional help for treatment. Professional pest control companies offer several treatment options, including:
- Liquid treatments: This involves injecting a liquid insecticide into the soil around your home’s foundation.
- Baiting systems: This involves placing bait stations around your home that contain a slow-acting insecticide.
- Fumigation: This is a more drastic treatment that involves sealing your home and fumigating it with a gas insecticide.
Termites can cause significant damage to your home, so it’s important to be aware of the signs of an infestation and take steps to prevent or treat it.
Knowing how do termites look like can be invaluable for preventing or addressing an infestation. By understanding their behavior and identifying them correctly, you can protect your home and your investment.
termites are they tiny ants or something else entirely
You might think of termites as tiny, destructive insects, but the truth is, these creatures are far more fascinating than you might imagine. “Termites the hidden critters you won’t believe exist” is a phrase that accurately reflects their secret world, filled with complex social structures, unique adaptations, and even surprising benefits to the environment. Let’s delve into the intriguing world of termites, uncovering the secrets these tiny creatures have been keeping for millions of years.
More Than Just Pests: The Hidden Wonders of Termites
Termites, often referred to as “white ants,” are a group of social insects that play a crucial role in the ecosystem. These tiny creatures, belonging to the order Isoptera, are found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. They are known for their remarkable ability to break down wood, playing a vital role in the decomposition of dead trees and returning nutrients to the soil. But their hidden world goes far beyond simply being nature’s recyclers.
The Termite Society: A Complex and Organized World
“Termites the hidden critters you won’t believe exist” are not just individuals; they are part of a highly organized and complex society. Like ants, termites live in colonies, with each member playing a specific role. The colony is divided into three main castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives.
- Workers: These are the most numerous and are responsible for the essential tasks of foraging for food, building and maintaining the nest, and caring for the young.
- Soldiers: These are the defenders of the colony, armed with powerful jaws or sticky secretions to ward off predators and intruders.
- Reproductives: The king and queen are responsible for reproduction, ensuring the continuation of the colony. The queen can live for decades and lay millions of eggs during her lifetime.
Termites: Architects of Incredible Structures
The ability of termites to construct elaborate nests is truly remarkable. “Termites the hidden critters you won’t believe exist” often create mounds that can reach towering heights. These mounds are not just shelters, they are marvels of engineering, designed to regulate temperature and humidity, and provide a safe haven for the colony. Termites are also known for their intricate underground networks of tunnels, which can extend for hundreds of meters, connecting different parts of the colony.
Termites: More Than Just Destructive Pests
While termites are known for their destructive potential, causing significant damage to wooden structures, they also provide several ecological benefits.
- Soil Enrichment: Termites play a vital role in soil aeration and nutrient cycling. Their constant tunneling and foraging activities break down organic matter, improving soil quality and promoting plant growth.
- Food Source: Termites are a crucial food source for numerous animals, including anteaters, armadillos, and birds. Their role in the food web is essential for maintaining ecological balance.
- Decomposers: Termites are essential decomposers, breaking down dead wood and other organic matter, helping to return nutrients to the environment. This process is vital for the health of forests and other ecosystems.
Unraveling the Secrets: Termites’ Hidden World
While we may think of termites as simple pests, their intricate world is a fascinating testament to the complexity of nature. From their social structures to their unique adaptations, these tiny creatures have a lot to teach us. “Termites the hidden critters you won’t believe exist” are a reminder that even the smallest creatures can have a significant impact on our environment. So the next time you see a termite mound, take a moment to appreciate these remarkable creatures and the hidden world they inhabit.
More About Termites:
By understanding these amazing creatures, we can learn to appreciate their role in the ecosystem and find ways to co-exist with them, minimizing potential damage while appreciating their valuable contribution to the natural world.
Termite Look-Alikes: Q&A
Q1: Are termites actually ants?
A: While they share some similarities, termites are not ants. They belong to a different order of insects called Isoptera. Though ants and termites both live in colonies and have a caste system, they have different physical characteristics and life cycles.
Q2: What do termites look like?
A: Termites come in various sizes and colors, but most have a soft, pale body with a straight, narrow waist. They are often described as “pale” and can be white, cream, brown, or black.
Q3: What are the different types of termites and how can I tell them apart?
A: There are three main types of termites: subterranean, drywood, and dampwood.
- Subterranean: The most common type, they have soft, pale bodies and are usually white or cream in color.
- Drywood: These are darker than subterranean termites, usually brown or black, and have a more robust build.
- Dampwood: They are larger than other termites and have darker bodies.
Q4: What do termite wings look like?
A: Termite wings are long and narrow, and equal in size. They are thin and translucent, and easily break off when flying.
Q5: How do I tell if a bug is a termite or an ant?
A: Look at the waist: Termites have a straight, narrow waist, while ants have a constricted, “pinched” waist.
Q6: What are termite soldiers like?
A: Termite soldiers are larger than workers and have strong mandibles used to defend the colony. They usually have a large head and can be white, cream, brown, or black.
Q7: What is the best way to identify termites?
A: If you suspect you have termites, it’s best to contact a professional pest control company for an accurate identification and treatment plan. They have the expertise and equipment to identify termites effectively.
Q8: How big are termites?
A: Termites can vary in size, but most are small – about ¼ to ½ inch long.
Q9: Do termites have antennae?
A: Yes, termites have long, bead-like antennae.
Q10: Can I treat termites myself?
A: While some DIY solutions exist, it’s recommended to contact a professional for the best results and to ensure the infestation is properly treated. Termite infestations can be complex, and professional treatment can prevent further damage to your property.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding termite morphology is crucial for early detection and prevention of infestations. Remember, termites come in various sizes, shapes, and colors, but their key features – soft bodies, straight antennae, and a distinct waist – remain consistent. By recognizing these characteristics, you can identify potential termite activity in your home and take immediate action to protect your property.
Now that you’ve learned about the unique physical traits of termites, share your thoughts! Have you ever encountered a termite infestation? What steps did you take to resolve it? Share your experiences and advice in the comments below. Don’t forget to spread the word and share this post on social media to help others learn about termite identification and keep their homes safe from these destructive pests.