A diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis helps visualize these crucial processes. We see how plants use sunlight to make food, releasing oxygen. This process fuels the world’s ecosystems.
Animals, including humans, then use this oxygen to break down food, releasing energy they need to live. This energy powers all life functions, from movement to growth. Understanding these diagrams reveals the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth
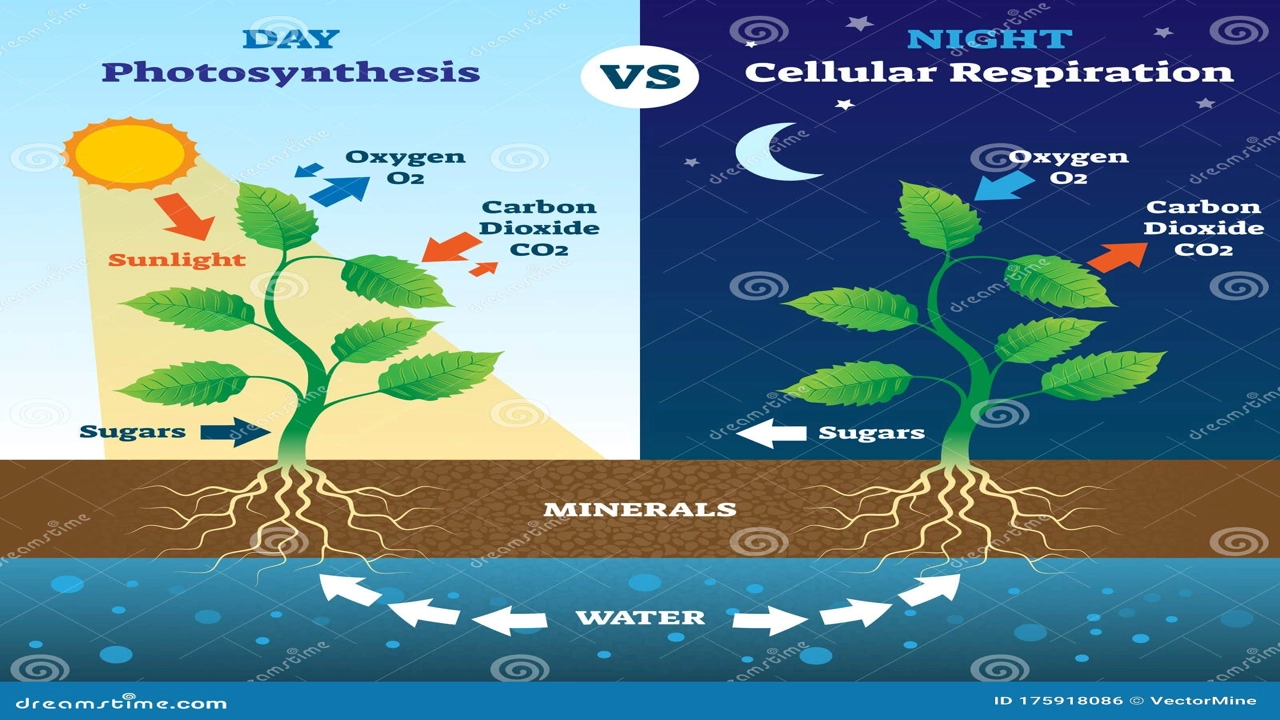
Let’s dive into the intricate dance of life: the interconnected processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. A diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis is a powerful tool for understanding this vital interplay. Finding a good visual representation is key, and we’ll explore why.
Understanding the Need for a Diagram Showing Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
We often learn about photosynthesis and cellular respiration separately. They’re presented as distinct processes, but in reality, they are deeply intertwined, forming a cyclical relationship vital for maintaining life on Earth. This is why a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis side-by-side offers such a crucial advantage. It allows us to grasp the elegant balance between these two fundamental biological pathways. Searching for “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” online brings up numerous options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Photosynthesis: Capturing the Sun’s Energy
Plants, algae, and some bacteria are the masters of photosynthesis. They use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (a simple sugar) and oxygen. This process takes place within specialized structures called chloroplasts. Think of it as nature’s way of converting solar energy into chemical energy. A diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis clearly illustrates this conversion. Locating a useful diagram will reveal the details of this process, including the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Remember when you search online, use the full query “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” for the best results.
- Light-dependent reactions: These capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): These use the ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
Understanding these steps is crucial to fully appreciate the intricate workings of photosynthesis. A comprehensive search for “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” will help you find diagrams that break down these steps effectively.
Cellular Respiration: Releasing Stored Energy
Cellular respiration is the reverse process of photosynthesis. Organisms, including plants and animals, break down glucose to release the stored energy. This energy is used to fuel various cellular processes, essential for growth, movement, and other life functions. This happens primarily in the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell. A diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis will clearly showcase this energy transfer. When looking for a diagram, make sure it depicts the main steps of cellular respiration:
- Glycolysis: The initial breakdown of glucose into pyruvate in the cytoplasm.
- Krebs cycle (Citric acid cycle): Further breakdown of pyruvate in the mitochondria, releasing carbon dioxide and generating ATP and electron carriers.
- Electron transport chain: A series of reactions within the mitochondria that generate the majority of ATP.
The oxygen we breathe is crucial for this process, and it’s the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Searching for “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” will help you visualize the intricate flow of energy and matter in this process.
The Interconnection: A Cycle of Life
The crucial point about finding a good “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” is understanding the cyclical relationship between these two processes. The glucose produced during photosynthesis serves as the primary fuel source for cellular respiration. The oxygen released during photosynthesis is essential for cellular respiration. In turn, the carbon dioxide released during cellular respiration is a vital reactant in photosynthesis. This beautiful, interwoven system maintains the balance of life on Earth. Searching online for “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis side by side” often yields better results if you want to specifically emphasize this relationship. This approach will highlight the reciprocal nature of these processes. You might also search for “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis and their relationship” to find diagrams that explicitly call out this connection.
Looking for “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis in simple terms” is a valid strategy if you are new to the subject. Simpler diagrams may omit some details but offer a clear and concise overview of the main concepts. Many resources on the internet, including educational websites and textbooks, provide this type of visual aid.
Finding the Right Diagram: Tips and Tricks
Finding the ideal “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” depends on your needs. Some diagrams are highly detailed, showing the precise chemical reactions involved. Others provide a more simplified overview. Consider your current understanding of the processes when searching. Start with a simple diagram if you are a beginner.
- Check the source: Ensure the diagram comes from a reputable source like an educational website, textbook, or scientific publication. This guarantees accuracy and clarity.
- Look for interactive diagrams: Some online diagrams allow you to click on different components to learn more about them.
- Consider the level of detail: Choose a diagram with the appropriate level of detail for your understanding and learning goals.
A clear understanding of photosynthesis and cellular respiration is fundamental to grasping many aspects of biology and ecology. Use the power of visual aids like diagrams to enhance your learning. Remember to use specific search terms like “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” to effectively locate the resources you need. Refine your search with terms like “simplified,” “side-by-side,” or “with labels” to find exactly the diagram that suits your purposes. Exploring different visuals will solidify your understanding of this crucial biological dance. Keep in mind that “a diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis” is your key to unlocking this knowledge.
photosynthesis vs respiration which wins
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration: two processes fundamental to life on Earth, yet often misunderstood as opposing forces. The truth, however, is far more intricate and fascinating than a simple “versus” implies. Let’s delve into the details behind the search query “photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth.”
Understanding Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, simply put, is how plants and some other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy. Think of it as nature’s solar power plant. Using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, these organisms produce glucose (a sugar) and oxygen. This glucose serves as their food source, providing the energy needed for growth and other life functions. The oxygen, a byproduct, is released into the atmosphere—the very air we breathe. This is a critical point often missed when exploring “photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth.” We depend directly on this process for survival.
The Cellular Respiration Counterpart
Cellular respiration, on the other hand, is the process by which organisms break down glucose to release energy. It’s the opposite of photosynthesis, in a way. This process occurs in nearly all living organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. They take in glucose and oxygen and produce energy (ATP), water, and carbon dioxide. This energy fuels all the life processes from movement to cell division. Again, understanding this is crucial to understanding “photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth.”
The Intertwined Dance of Life
The “shocking truth” regarding photosynthesis vs cellular respiration is their intricate interdependence. They’re not adversaries; they’re partners in a continuous cycle. Plants perform photosynthesis, creating the glucose that animals use for cellular respiration. Animals, in turn, exhale carbon dioxide, which plants utilize for photosynthesis. It’s a beautifully balanced system, highlighting the remarkable interconnectedness of life. Search queries like “photosynthesis and cellular respiration relationship” or “how photosynthesis and cellular respiration work together” reveal this symbiotic relationship.
Key Differences Highlighted
While both processes involve energy transformations, there are some key distinctions:
- Energy Source: Photosynthesis uses light energy, while cellular respiration uses chemical energy (from glucose).
- Products: Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen. Cellular respiration produces ATP (energy), water, and carbon dioxide.
- Location: Photosynthesis primarily takes place in chloroplasts (in plant cells), cellular respiration mainly occurs in mitochondria (in most cells).
Exploring Common Misconceptions
Many misunderstandings surround “photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth.” For example, some believe that they are entirely separate processes, unrelated to each other. Others might think cellular respiration is only for animals. The reality is much more nuanced and interconnected, forming a life-sustaining cycle.
Further Research and Related Searches
To further your understanding, consider researching these related topics:
- Photosynthesis equation
- Cellular respiration equation
- The role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis
- Anaerobic respiration
- The importance of oxygen in cellular respiration
- Photosynthesis vs chemosynthesis
- Light-dependent reactions
- Light-independent reactions
Delving into these related areas helps paint a complete picture, unraveling the mysteries behind the search query “photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth.” It reveals the elegant, essential relationship that sustains life on this planet, a relationship much more profound than a simple opposition.
Understanding the intricacies of photosynthesis vs cellular respiration, the shocking truth about their interdependence, is fundamental to appreciating the delicate balance of life on Earth. The search query “photosynthesis vs cellular respiration the shocking truth” leads to a deeper appreciation of the complexity and beauty of natural processes.
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis: Q&A
Q1: What is the main goal of photosynthesis?
A1: Plants use photosynthesis to make their own food, a type of sugar, using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
Q2: What happens to the sugar made during photosynthesis?
A2: The plant uses the sugar for energy and building materials to grow. It can also store the sugar for later use.
Q3: What does a plant need to perform photosynthesis?
A3: A plant needs sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to conduct photosynthesis.
Q4: What is the main goal of cellular respiration?
A4: Cellular respiration breaks down sugar to release the energy stored within it. This energy powers the plant’s life processes.
Q5: What are the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration?
A5: Plants use sugar and oxygen as inputs for cellular respiration. They produce energy, water, and carbon dioxide as outputs.
Q6: Do plants perform both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
A6: Yes, plants perform both processes. Photosynthesis makes the sugar needed for cellular respiration, and cellular respiration provides the energy the plant needs to live.
Q7: How do animals get the energy they need?
A7: Animals obtain energy by consuming plants or other animals that have consumed plants. Their bodies perform cellular respiration to break down the sugars in their food for energy.
Q8: Where in the plant cell does photosynthesis take place?
A8: Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, which are special structures inside plant cells.
Q9: Where in the plant cell does cellular respiration occur?
A9: Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria, another structure inside plant cells.
Q10: Is carbon dioxide a waste product in photosynthesis or cellular respiration?
A10: Carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration, but it’s a necessary input for photosynthesis.
Conclusion
The diagram clearly illustrates the interconnectedness of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Plants use sunlight to create sugars, storing energy in the process. Animals then consume these plants, breaking down the sugars through respiration to release that stored energy for their own life processes. This reciprocal relationship highlights the fundamental importance of both processes for sustaining life on Earth. We see how energy flows from the sun, through plants, and finally to animals, forming a beautiful and crucial cycle.
Understanding these basic processes offers a deeper appreciation for the natural world around us. The intricate dance of energy conversion between plants and animals is fascinating and vital. We encourage you to share your thoughts on this relationship, perhaps reflecting on other examples of such symbiotic cycles in nature. Please spread the word about this post by sharing it on your favorite social media platform. Let’s continue this conversation about the wonders of cellular processes!




